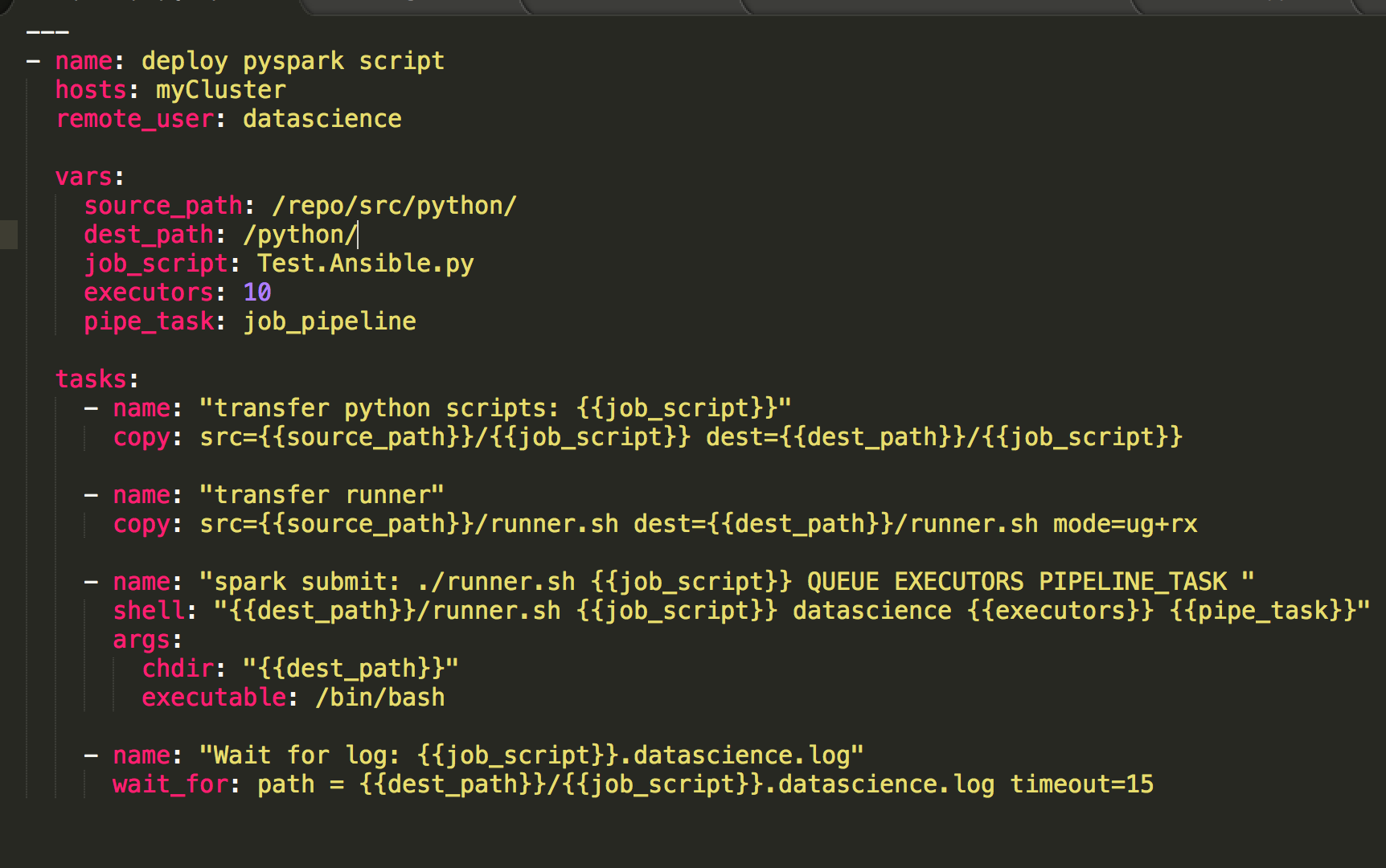
Ansible 2.5 and above work with Python 3. Previous to 2.5, using Python 3 wasconsidered a tech preview. This topic discusses how to set up your controller and managed machinesto use Python 3.
Import ansiblerunner: def run: # create an Ansible playbook as a native Python dict object. Currently # ansible-runner does not validate the playbook structure so it needs to be # correct when passed in otherwise ansible will fail. Playbook = 'hosts': 'eos', 'gatherfacts': False, 'roles': 'name': 'ansible-eos', 'function': 'clear.
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages. Files for ansible-playbook-runner, version 0.1.2. Python API pre 2.0 ¶. It’s pretty simple: import ansible.runner runner = ansible.runner.Runner ( modulename='ping', moduleargs=', pattern='web.', forks=10 ) datastructure = runner.run The run method returns results per host, grouped by whether they could be contacted or not. Return types are module specific, as expressed in the About. A tool and python library that helps when interfacing with Ansible https://github.com/ansible/ansible-runner.
Note
On the controller we support Python 3.5 or greater and Python 2.7 or greater. Module-side, we support Python 3.5 or greater and Python 2.6 or greater.
On the controller side
The easiest way to run /usr/bin/ansible under Python 3 is to install it with the Python3version of pip. This will make the default /usr/bin/ansible run with Python3:
If you are running Ansible Running the devel branch from a clone and want to use Python 3 with your source checkout, run yourcommand via python3. For example:
Note
Individual Linux distribution packages may be packaged for Python2 or Python3. When running fromdistro packages you’ll only be able to use Ansible with the Python version for which it wasinstalled. Sometimes distros will provide a means of installing for several Python versions(via a separate package or via some commands that are run after install). You’ll need to checkwith your distro to see if that applies in your case.
Using Python 3 on the managed machines with commands and playbooks
Ansible will automatically detect and use Python 3 on many platforms that ship with it. To explicitly configure aPython 3 interpreter, set the
ansible_python_interpreterinventory variable at a group or host level to thelocation of a Python 3 interpreter, such as /usr/bin/python3. The default interpreter path may also beset inansible.cfg.
See also
Interpreter Discovery for more information.
See also
How to build your inventory for more information.
Run your command or playbook:
Note that you can also use the -e command line option to manuallyset the python interpreter when you run a command. This can be useful if you want to test whethera specific module or playbook has any bugs under Python 3. For example:
What to do if an incompatibility is found

We have spent several releases squashing bugs and adding new tests so that Ansible’s core featureset runs under both Python 2 and Python 3. However, bugs may still exist in edge cases and many ofthe modules shipped with Ansible are maintained by the community and not all of those may be portedyet.
If you find a bug running under Python 3 you can submit a bug report on Ansible’s GitHub project. Be sure to mention Python3 in the bug report sothat the right people look at it.
If you would like to fix the code and submit a pull request on github, you canrefer to Ansible and Python 3 for information on how we fixcommon Python3 compatibility issues in the Ansible codebase.
In the following tutorial, we will understand Ansible along with its benefits and how we can use Ansible in Python.
An Introduction to Ansible
Ansible is an open-source platform or automation tool utilized to perform IT tasks like deploying applications, managing configurations, orchestrating intra-service, and provisioning. Automation is the key as time passes by, with a highly complex environment of Information Technologies that often require to scale too quickly for developers and system administrators in order to work along if they had to perform every function manually. Automation helps in simplifying the intricate tasks and makes the works of developers much manageable. It also allows the developers to focus attention on other activities that include values to an organization. In other terms, Automation increases efficiency by freeing up time. And Ansible, as stated above, is among the swiftly rising tools in the era of Automation.
Python Ansible Runner 2
What is Ansible?
- Ansible is a push-based Infrastructure as code (IaC) that provides a user-friendly domain-specific language so we can define the architecture as per desire in a declarative way.
- The term push-based signifies that Ansible utilizes SSH to communicate among the machine executing Ansible and the machines where the configurations are being applied.
- The machines working with Ansible that we like to configure are known as managed nodes or Ansible hosts. In terms of Ansible, the list of hosts is known as an inventory.
- The machine reading the definition files and executing Ansible in order to push the configuration to the host is known as a control node.
- Ansible is written in the Python programming language and has a quite minimal learning curve. The procedure to set up Ansible is pretty simple and doesn't rely on any extra application, servers, or client daemons.
- Ansible is based on the principle of embracing the interrelation and architecture of the system. Like other tools used for managing configuration (such as Puppet, Chef, or Salt), it works with two types of servers: controlling machines and nodes.
- Ansible uses small programs known as Ansible Modules in order to orchestrate nodes. These modules are the resource models of the chosen system state executed over SSH. We do not need any agents and extra custom security infrastructure for this purpose.
- The library of modules can exist in any machine. The modules perform tasks using JSON protocol over the standard output and write the convenient code in any programming language, including Python.
- The system utilizes YAML in Ansible playbooks format in order to describe the work for Automation. This way, it is the machine as well as human-friendly. And when the nodes are not being managed by Ansible, it doesn't consume resources since neither programs nor daemons are running in the background.
Some Benefits of Ansible
Being a powerful automation engine, Ansible helps developers in deploying software more efficiently. We can avoid agents, custom code, or custom scripting and mainly focus on security, easy audibility, review, and rewriting of the content. There are numerous advantages of Ansible over similar platforms used for software automation. Some of these advantages are described below:
- Simplicity:Ansible provides simplicity as the developers do not require writing scripts or custom code for the deployment of the applications and updating them. It allows Automation in a language approaching plain English. It is easy for developers, system administrators, and IT managers to read, manage and speed up their projects and programs.
- Completeness:Ansible also provides completeness as it comes combined with different complex tools for managing configuration, deploying applications, orchestrating workflow, and even cloud provisioning in a single system. Modules help in automating nearly everything out-of-the-box, and no extra application is required.
- Secureness:Ansible utilizes SSH, so it doesn't deploy vulnerable agents to nodes and doesn't require daemons on root-level or extra ports. Ansibles offers an agentless environment that helps in improving security and can be usable as non-root. Ansible features in-built authentication for Operating System, support for LDAP, SSSD, and Kerberos.
Understanding the Python API for Ansible Purpose
We can call Ansible code using Python using the Application Programming Interface (API) of Ansible. Ansible has released version 2.0 of its API that allows better integration with different programming languages. It is quite a significant aspect to note that Ansible has extended its capability in order to support development with the help of Python; however, it is also mentioned on its website that it can also stop supporting the API framework on the basis of its own discretion (creating or even fixing a bug in the current version of API).
There are different methods available for the developers to utilize Ansible from an Application Programming Interface (API) perspective. We can utilize the Ansible API for the Python programming language that allows us to control nodes. We can extend Ansible to respond to different events in Python, write plugins and plugin inventory data from external sources of data.